How to Read Json File Returned by Restful Web Service C#
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Swallow a RESTful spider web service
 Download the sample
Download the sample
Integrating a spider web service into an application is a common scenario. This article demonstrates how to consume a RESTful spider web service from a Xamarin.Forms application.
Representational Land Transfer (REST) is an architectural fashion for building spider web services. REST requests are made over HTTP using the aforementioned HTTP verbs that web browsers utilise to think web pages and to send data to servers. The verbs are:
- GET – this operation is used to retrieve data from the web service.
- Post – this operation is used to create a new item of information on the web service.
- PUT – this operation is used to update an item of data on the web service.
- PATCH – this operation is used to update an detail of data on the web service by describing a fix of instructions about how the item should be modified. This verb is not used in the sample application.
- DELETE – this operation is used to delete an detail of data on the web service.
Web service APIs that adhere to Residual are called RESTful APIs, and are divers using:
- A base URI.
- HTTP methods, such every bit GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, or DELETE.
- A media type for the data, such as JavaScript Object Notation (JSON).
RESTful web services typically use JSON messages to return data to the client. JSON is a text-based data-interchange format that produces compact payloads, which results in reduced bandwidth requirements when sending data. The sample application uses the open source NewtonSoft JSON.Cyberspace library to serialize and deserialize messages.
The simplicity of REST has helped go far the master method for accessing web services in mobile applications.
When the sample application is run, it volition connect to a locally hosted REST service, as shown in the following screenshot:
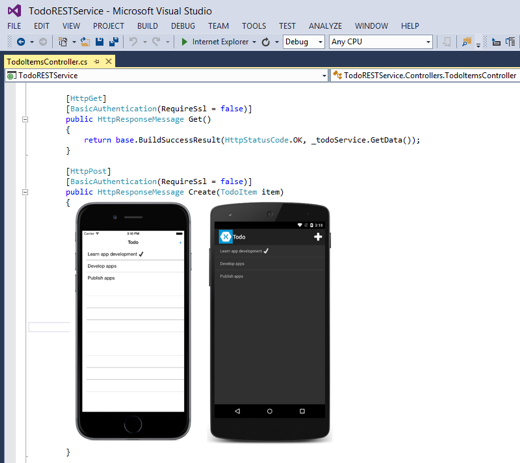
Notation
In iOS 9 and greater, App Transport Security (ATS) enforces secure connections betwixt internet resources (such every bit the app'southward back-cease server) and the app, thereby preventing accidental disclosure of sensitive information. Since ATS is enabled by default in apps built for iOS 9, all connections will be subject to ATS security requirements. If connections do not meet these requirements, they will fail with an exception.
ATS tin be opted out of if it is not possible to use the HTTPS protocol and secure communication for cyberspace resources. This can be achieved past updating the app's Info.plist file. For more than data run across App Transport Security.
Eat the web service
The Residuum service is written using ASP.NET Cadre and provides the following operations:
| Operation | HTTP method | Relative URI | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Go a list of to-do items | GET | /api/todoitems/ | |
| Create a new to-do item | Post | /api/todoitems/ | A JSON formatted TodoItem |
| Update a to-do particular | PUT | /api/todoitems/ | A JSON formatted TodoItem |
| Delete a to-practice item | DELETE | /api/todoitems/{id} |
The majority of the URIs include the TodoItem ID in the path. For instance, to delete the TodoItem whose ID is 6bb8a868-dba1-4f1a-93b7-24ebce87e243, the client sends a DELETE request to http://hostname/api/todoitems/6bb8a868-dba1-4f1a-93b7-24ebce87e243. For more data near the information model used in the sample awarding, run across Modeling the data.
When the Spider web API framework receives a request it routes the request to an action. These actions are simply public methods in the TodoItemsController class. The framework use routing middleware to match the URLs of incoming requests and map them to actions. REST APIs should use attribute routing the model the app's functionality as a set of resources whose operations are represented by HTTP verbs. Attribute routing uses a fix of attributes to map actions directly to route templates. For more information near attribute routing, see Aspect routing for REST APIs. For more information about building the Residuum service using ASP.NET Core, see Creating Backend Services for Native Mobile Applications.
The HttpClient course is used to send and receive requests over HTTP. It provides functionality for sending HTTP requests and receiving HTTP responses from a URI identified resources. Each request is sent equally an asynchronous operation. For more information about asynchronous operations, see Async Support Overview.
The HttpResponseMessage class represents an HTTP response message received from the spider web service later an HTTP request has been fabricated. It contains information near the response, including the status code, headers, and any body. The HttpContent form represents the HTTP body and content headers, such as Content-Type and Content-Encoding. The content can be read using whatever of the ReadAs methods, such as ReadAsStringAsync and ReadAsByteArrayAsync, depending upon the format of the data.
Create the HTTPClient object
The HttpClient instance is declared at the form-level so that the object lives for equally long as the application needs to make HTTP requests, every bit shown in the post-obit code example:
public class RestService : IRestService { HttpClient client; ... public RestService () { client = new HttpClient (); ... } ... } Recall information
The HttpClient.GetAsync method is used to transport the GET asking to the spider web service specified by the URI, and then receive the response from the web service, equally shown in the following code instance:
public async Task<List<TodoItem>> RefreshDataAsync () { ... Uri uri = new Uri (string.Format (Constants.TodoItemsUrl, string.Empty)); ... HttpResponseMessage response = expect client.GetAsync (uri); if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode) { string content = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync (); Items = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<List<TodoItem>>(content, serializerOptions); } ... } The REST service sends an HTTP status lawmaking in the HttpResponseMessage.IsSuccessStatusCode property, to indicate whether the HTTP request succeeded or failed. For this operation the REST service sends HTTP status lawmaking 200 (OK) in the response, which indicates that the request succeeded and that the requested information is in the response.
If the HTTP operation was successful, the content of the response is read, for display. The HttpResponseMessage.Content property represents the content of the HTTP response, and the HttpContent.ReadAsStringAsync method asynchronously writes the HTTP content to a cord. This content is then deserialized from JSON to a List of TodoItem instances.
Warning
Using the ReadAsStringAsync method to retrieve a big response tin can have a negative performance bear upon. In such circumstances the response should be straight deserialized to avoid having to fully buffer information technology.
Create information
The HttpClient.PostAsync method is used to transport the POST request to the spider web service specified past the URI, and then to receive the response from the web service, equally shown in the following code example:
public async Task SaveTodoItemAsync (TodoItem particular, bool isNewItem = faux) { Uri uri = new Uri (string.Format (Constants.TodoItemsUrl, string.Empty)); ... cord json = JsonSerializer.Serialize<TodoItem>(particular, serializerOptions); StringContent content = new StringContent (json, Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"); HttpResponseMessage response = null; if (isNewItem) { response = expect client.PostAsync (uri, content); } ... if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode) { Debug.WriteLine (@"\tTodoItem successfully saved."); } ... } The TodoItem instance is serialized to a JSON payload for sending to the spider web service. This payload is then embedded in the trunk of the HTTP content that will be sent to the web service before the request is made with the PostAsync method.
The Rest service sends an HTTP status code in the HttpResponseMessage.IsSuccessStatusCode property, to indicate whether the HTTP request succeeded or failed. The common responses for this functioning are:
- 201 (CREATED) – the asking resulted in a new resource being created earlier the response was sent.
- 400 (BAD REQUEST) – the asking is not understood past the server.
- 409 (Disharmonize) – the request could not be carried out considering of a conflict on the server.
Update data
The HttpClient.PutAsync method is used to send the PUT request to the web service specified by the URI, and then receive the response from the web service, equally shown in the following code example:
public async Job SaveTodoItemAsync (TodoItem particular, bool isNewItem = false) { ... response = wait client.PutAsync (uri, content); ... } The performance of the PutAsync method is identical to the PostAsync method that'due south used for creating data in the spider web service. However, the possible responses sent from the web service differ.
The Residuum service sends an HTTP status code in the HttpResponseMessage.IsSuccessStatusCode property, to indicate whether the HTTP request succeeded or failed. The common responses for this operation are:
- 204 (NO CONTENT) – the request has been successfully processed and the response is intentionally blank.
- 400 (BAD Asking) – the request is non understood by the server.
- 404 (NOT FOUND) – the requested resources does not exist on the server.
Delete data
The HttpClient.DeleteAsync method is used to send the DELETE request to the spider web service specified by the URI, and and so receive the response from the spider web service, as shown in the post-obit code example:
public async Task DeleteTodoItemAsync (string id) { Uri uri = new Uri (string.Format (Constants.TodoItemsUrl, id)); ... HttpResponseMessage response = await customer.DeleteAsync (uri); if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode) { Debug.WriteLine (@"\tTodoItem successfully deleted."); } ... } The Remainder service sends an HTTP status lawmaking in the HttpResponseMessage.IsSuccessStatusCode property, to indicate whether the HTTP request succeeded or failed. The common responses for this operation are:
- 204 (NO CONTENT) – the asking has been successfully candy and the response is intentionally blank.
- 400 (BAD REQUEST) – the request is not understood by the server.
- 404 (NOT Constitute) – the requested resource does not exist on the server.
Local evolution
If you are developing your Balance spider web service locally with a framework such as ASP.Net Core Web API, you can debug your spider web service and mobile app at the aforementioned time. In this scenario you lot must enable clear-text HTTP traffic for the iOS simulator and Android emulator. For information nearly configuration your project to let advice, come across Connect to local web services.
- Microsoft Larn: Consume Rest web services in Xamarin Apps
- Microsoft Learn: Create a web API with ASP.NET Cadre
- Creating Backend Services for Native Mobile Applications
- Attribute routing for Residuum APIs
- TodoREST (sample)
- HttpClient API
- Android Network Security Configuration
- iOS App Send Security
- Connect to local web services
Feedback
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/xamarin/xamarin-forms/data-cloud/web-services/rest
0 Response to "How to Read Json File Returned by Restful Web Service C#"
Post a Comment